Key Takeaways
- Couverture chocolate contains a higher percentage of cocoa butter (32-39%) than regular chocolate, resulting in superior melting properties and flavor
- Proper tempering is essential when working with couverture chocolate to achieve the perfect shine, snap, and stability
- Available in dark, milk, white, and ruby varieties, each with distinct flavor profiles and applications
- Professional chocolatiers and pastry chefs prefer couverture chocolate for its workability and luxurious mouthfeel
- Quality couverture requires proper storage between 60-68°F (15-20°C) in a dry environment away from strong odors
- Explore premium couverture chocolate options at Zucchero Canada for your next chocolate creation
Couverture Chocolate
In the world of professional chocolate making, couverture chocolate stands as the gold standard that separates amateur enthusiasts from skilled artisans. This premium chocolate variety has earned its reputation through exceptional quality, superior workability, and the ability to create stunning confections that command premium pricing.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore everything you need to know about couverture chocolate—from its unique composition and varieties to proper handling techniques and creative applications. Whether you're a professional pastry chef, an enthusiastic home baker, or simply a chocolate connoisseur, understanding couverture chocolate will elevate your appreciation and mastery of fine chocolate.
What Is Couverture Chocolate?
Couverture chocolate (pronounced "koo-vehr-TYOOR") derives its name from the French word "couvrir," meaning "to cover" or "coat." This etymology perfectly captures its primary purpose: creating flawless coatings, elegant mouldings, and professional-quality chocolate applications that showcase true craftsmanship.
The fundamental distinction between couverture and regular chocolate lies in cocoa butter content. While standard eating chocolate contains approximately 15-18% cocoa butter, chocolate couverture boasts significantly higher levels ranging from 31% to 39%. This additional cocoa butter transforms both the chocolate's behavior during processing and its final taste profile.
The Difference Between Couverture and Regular Chocolate
Understanding the distinctions between couverture chocolate and regular chocolate helps explain why professionals are willing to pay a premium for this specialized product:
Composition Differences
-
Couverture chocolate: Contains 32-39% cocoa butter, uses only genuine cocoa butter as the fat component, and typically includes premium cocoa beans
-
Regular chocolate: Contains about 25-30% cocoa butter and follows less stringent quality requirements
-
Compound chocolate: Contains vegetable fats instead of cocoa butter, making it easier to work with but significantly inferior in taste and texture
Performance Differences
-
Melting behavior: Couverture chocolate melts smoothly and evenly at a precise temperature due to its high cocoa butter content
-
Setting properties: When properly tempered, couverture forms stable, glossy surfaces with a clean snap
-
Mouthfeel: Couverture dissolves smoothly on the tongue, releasing complex flavor notes gradually
-
Flavor complexity: The higher quality ingredients and manufacturing processes result in more nuanced flavor profiles
Application Differences
-
Couverture chocolate: Ideal for enrobing, molding, dipping, and creating decorations where appearance and mouthfeel are paramount
-
Regular chocolate: Better suited for baking into cookies, cakes, and other applications where melting properties are less critical
-
Compound chocolate: Used primarily in commercial manufacturing where cost control and ease of handling outweigh quality concerns
Key Characteristics of Couverture Chocolate
High Cocoa Butter Content
The defining characteristic of couverture chocolate is its elevated cocoa butter percentage. This natural fat derived from cocoa beans gives couverture chocolate several advantages:
-
Lower melting point: Cocoa butter melts precisely at body temperature (around 93-95°F or 34-35°C), creating that sought-after "melt-in-your-mouth" sensation
-
Crystal structure: Cocoa butter forms complex crystalline structures when properly tempered, resulting in the characteristic shine and snap
-
Flavor carrier: Cocoa butter serves as an excellent medium for carrying and enhancing flavor compounds
-
Smooth texture: The higher fat content creates an unparalleled silky texture that coats the palate
Flavor Profiles
Couverture chocolate offers exceptional flavor complexity due to several factors:
-
Bean selection: Premium couverture often uses single-origin beans or carefully crafted blends
-
Processing methods: Conching (a mixing and aerating process) is typically carried out longer for couverture, developing more refined flavors
-
Minimal additives: Quality couverture contains fewer additives and emulsifiers that might mask natural chocolate notes
-
Flavor development: The higher cocoa butter content helps flavors develop and linger on the palate
Texture and Mouthfeel
The textural experience of couverture chocolate is distinctive and luxurious:
-
Clean snap: Properly tempered couverture breaks with a crisp, satisfying snap
-
Smooth dissolution: It melts evenly on the tongue without graininess
-
Cooling sensation: The rapid melting of cocoa butter creates a slight cooling effect in the mouth
-
Lingering finish: The flavor and texture experience continues after the chocolate has melted
Types of Couverture Chocolate
Dark Couverture
Dark couverture chocolate contains cocoa mass, cocoa butter, sugar, and usually a small amount of vanilla and lecithin. No milk solids are added. Key characteristics include:
-
Cocoa content: Typically ranges from 55% to 85% total cocoa solids
-
Flavor profile: Notes can range from fruity and acidic to earthy and roasted, depending on bean origin and processing
-
Best uses: Enrobing truffles, molding bonbons, making chocolate decorations, and applications where pure chocolate flavor is desired
-
Tempering range: Typically tempered to 88-90°F (31-32°C)
Milk Couverture
Milk couverture contains cocoa mass, cocoa butter, sugar, milk solids, and usually vanilla and lecithin. It offers:
-
Cocoa content: Usually between 30-45% total cocoa solids
-
Milk fat content: Additional milk fat affects flavor and tempering properties
-
Flavor profile: Creamier, sweeter, with caramel and dairy notes complementing the chocolate flavor
-
Best uses: Enrobing more delicate flavored centers, creating milk chocolate shells and decorations
-
Tempering range: Typically tempered to a slightly lower temperature of 86-88°F (30-31°C)
White Couverture
White couverture contains cocoa butter, sugar, milk solids, vanilla, and lecithin, but no cocoa solids. Its characteristics include:
-
Cocoa butter content: Must contain a minimum percentage of cocoa butter (typically at least 32%)
-
Flavor profile: Sweet, creamy, with vanilla notes and no chocolate flavor (as it contains no cocoa solids)
-
Best uses: Creating contrasting decorations, white chocolate shells, and coatings for visual appeal
-
Tempering range: The lowest tempering temperature at 84-86°F (29-30°C)
| Cocoa Content | Flavor Profile | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 54-60% | Balanced, approachable | Ganaches, mousses, general coating |
| 64-70% | Rich, complex | Truffles, high-end confections |
| 72-80% | Intense, sophisticated | Single-origin applications, advanced techniques |
| 85%+ | Very intense, minimal sweetness | Specialized applications, health-conscious products |
Couverture vs. Regular Chocolate: Key Differences
Understanding the distinctions between couverture chocolate and regular eating chocolate helps professionals make informed ingredient choices and set appropriate customer expectations.
Composition Differences
Regular Chocolate:
- 15-18% cocoa butter content
- Often contains vegetable fats as cost-reduction measures
- Formulated primarily for direct consumption
- May include stabilizers and preservatives
Couverture Chocolate:
- 31-39% cocoa butter content
- Pure cocoa butter without vegetable fat substitutions
- Optimized for processing and professional applications
- Minimal additives for clean flavor profiles
How to Use Couverture Chocolate
Confectionery and Truffles
Couverture chocolate excels in fine confectionery applications:
-
Molded bonbons: Creating thin, even shells in chocolate molds
-
Hand-dipped truffles: Enrobing ganache centers with a thin, snappy coating
-
Filled chocolates: Casting shells and filling with caramels, pralines, or liqueur fillings
-
Solid molded items: Creating solid chocolate figures with excellent shine and snap
Chocolate Decorations
The superior flow and setting properties make couverture ideal for decorative work:
-
Chocolate curls and shavings: Creating delicate decorations for dessert garnishes
-
Chocolate ribbons: Casting thin sheets for wrapping or decoration
-
Transfer sheets: Working with printed cocoa butter designs
-
Chocolate showpieces: Building elaborate display pieces for competitions or events
Enrobing and Dipping
Couverture's fluid properties when tempered make it perfect for coating:
-
Enrobed confections: Professionally coating caramels, nougats, and other centers
-
Dipped fruits: Creating chocolate-covered strawberries, orange peels, or other fruits
-
Cookie dipping: Partially coating cookies or biscuits with perfectly set chocolate
-
Nut coating: Enrobing nuts for chocolate-covered almonds, hazelnuts, etc.
Baking Applications
While primarily used for finishing touches, couverture can elevate baking:
-
Chocolate decor: Creating decorative elements for cakes and pastries
-
Ganache: Making superior ganache for cake filling or glazing
-
Mousse: Creating silky-smooth chocolate mousse with exceptional flavor
-
Baking pieces: Chopping into chunks for high-end cookies and brownies
Top Couverture Brands
Several manufacturers are renowned for their quality couverture products:
-
Valrhona (France)
-
Callebaut (Belgium)
-
Cacao Barry (France)
-
Guittard (USA)
-
Felchlin (Switzerland)
-
Zucchero Canada's premium chocolate collection features several exceptional couverture options
Conclusion: Elevating Your Chocolate Creations
Couverture chocolate represents the gold standard in the chocolate world, offering unparalleled quality, workability, and sensory experience. While it requires more careful handling than regular or compound chocolate, the results are well worth the extra attention.
For those serious about chocolate work, investing in quality couverture chocolate is essential. Zucchero Canada offers a curated selection of premium chocolate products, including fine couverture varieties perfect for both professional and ambitious home chocolatiers.
As you continue your chocolate journey, remember that practice is key to mastering the art of working with couverture chocolate. Each tempering session, each molding attempt, and each decorative element you create will build your skills and confidence. The reward—creating chocolate confections with professional shine, snap, and flavor—is truly satisfying for both creator and consumer.





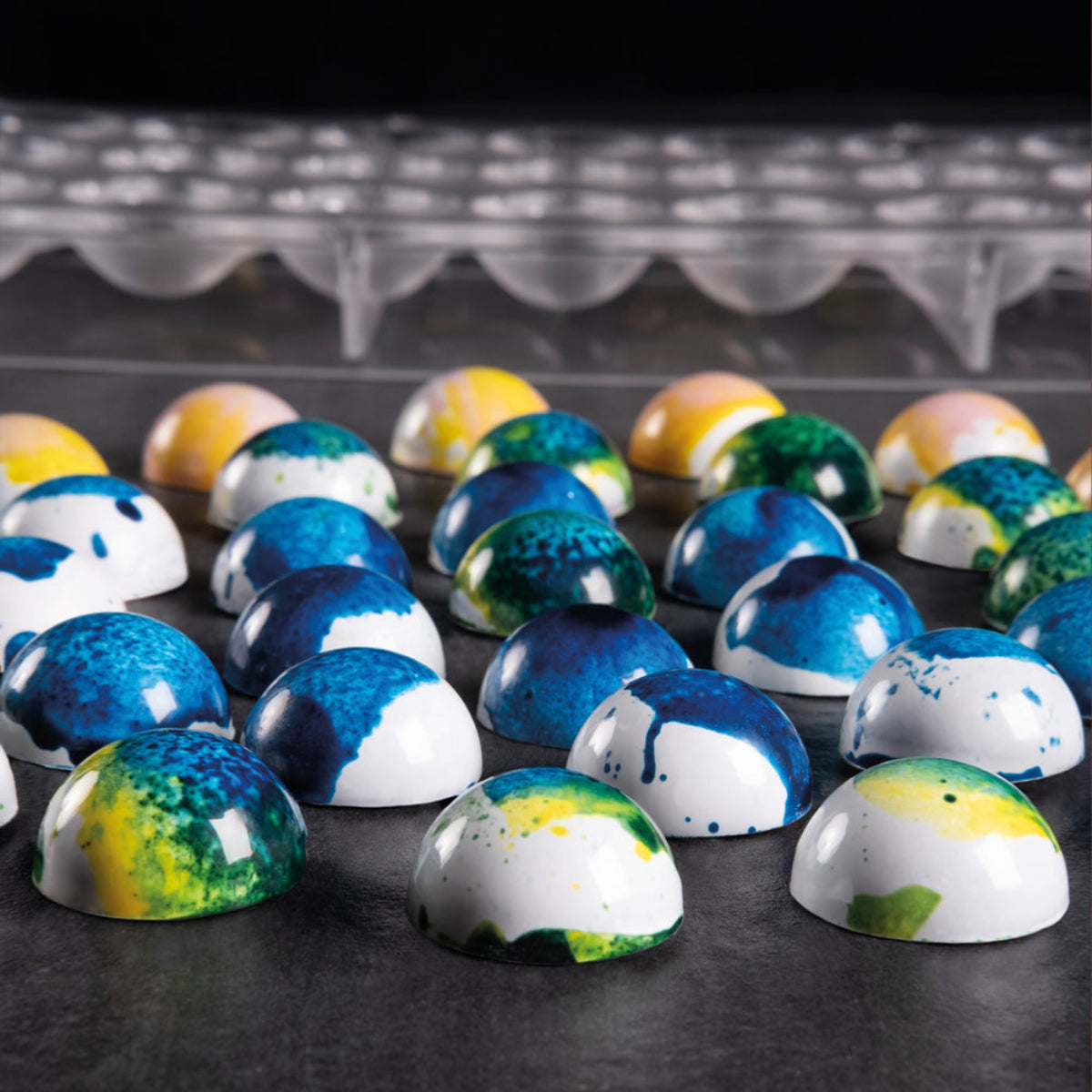




























Dejar un comentario
Todos los comentarios se revisan antes de su publicación.
Este sitio está protegido por hCaptcha y se aplican la Política de privacidad de hCaptcha y los Términos del servicio.